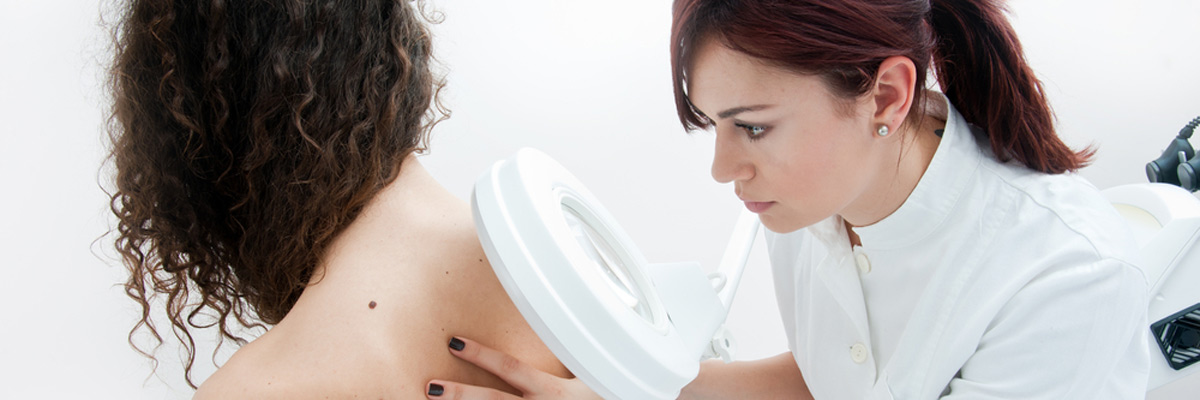
Recognizing the Early Signs of Cancer
We do not like to think about the possibility of cancer, but early detection of skin cancer can lead to successful treatment.
Actinic Keratosis, or AK, is a condition that typically comes from sun damage. Affected skin may appear as a crusty, scaly bump, red, pink, tan, or flesh-toned. AK lesions may also look flat or raised, rough in texture or solid, and may range in size from as small as one millimeter to as much as two centimeters.
To recognize Actinic Keratosis, touch may be the best sense to use. Lesions that feel rough, and itch periodically, or develop tenderness or a prickly sensation are a sign of AK. These spots develop most frequently on areas that get the most sun exposure, such as the:
- Scalp
- Ears
- Face
- Lips
- Neck
- Shoulders
- Forearms
- Back of hands
Are you at risk?
Actinic keratosis is primarily associated with sun exposure. To that end, we all have some degree of risk of developing these lesions. However, certain factors increase susceptibility, such as complexion; light-eyed, fair-skinned people are more likely to experience this condition. Medical disorders that make a person more sensitive to the sun also increase risk, as does age. According to the American Academy of Dermatology, 60 percent of predisposed individuals, age forty and over, will develop one or more AK lesions.